Crew Studies Space Orientation, DNA Data Storage as Dragon Reboosts Station
The Expedition 73 crew ended the work week exploring how living and working in space affects the sensory system and DNA. The International Space Station residents also continued researching how digestion is impacted by microgravity and unpacking a U.S. cargo craft.
A pair of experiments taking place simultaneously aboard the orbital outpost on Friday used two different sets of virtual reality goggles to examine how astronauts adjust to the lack of an up-and-down reference in microgravity. The vestibular system helps humans on Earth stand upright, keep their balance, and maintain a sense of motion. Those signals change in space as an astronaut’s brain adjusts to weightlessness and begins relying on visual tracking and muscle memory to figure out balance and spatial orientation.
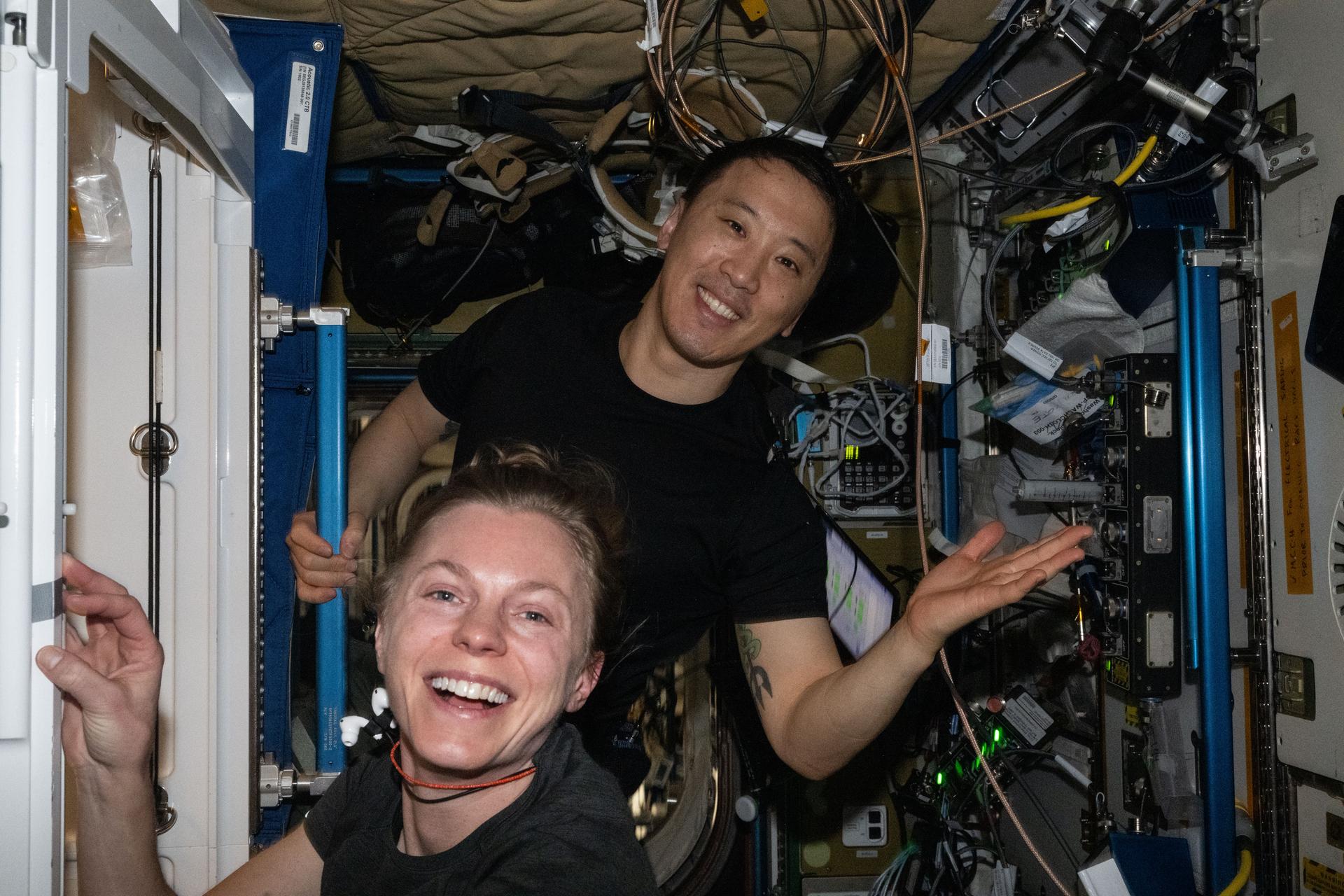
NASA Flight Engineers Zena Cardman and Jonny Kim joined each other in Columbus laboratory module and explored what happens to the structure of the vestibular system, such as the inner ear, fluid, and tiny hairs, that detects gravity and movement when living off the Earth. Cardman operated computer software that sent visual stimuli to a virtual reality headset that Kim was wearing as doctors on the ground monitored his eye movements and other responses for the CIPHER human research study. The data will inform countermeasures to space dizziness, help crews train for longer missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond, and prepare astronauts for the return to Earth after months or years in space.
Afterward, Kim sequenced DNA samples in the Harmony module for a biotechnology study investigating using DNA as a way to store and encrypt digital data to reduce reliance on traditional and heavier storage methods in space. Cardman worked in the Kibo laboratory module servicing scientific samples stowed inside combustion research hardware.
Roscosmos cosmonaut Oleg Platonov wore virtual reality glasses for another sensory system study that took place in the Nauka science module. Platonov responded to computer-generated visual stimuli as his eye movements and other physiological reactions were monitored. Once again, results from the experiment may improve crew training techniques, help with the readaptation to Earth’s gravity, as well as advance treatments for balance disorders on Earth.
Flight Engineers Mike Fincke of NASA and Kimiya Yui of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) partnered together on Friday continuing to unload new science and supplies delivered aboard the Cygnus XL cargo craft on Sept. 18. Fincke earlier installed a CubeSat on the NanoRacks external platform that will soon be placed outside the space station. The CubeSat will be deployed into Earth orbit to test plasma propulsion. Yui configured a pressure management device in the Tranquility module then downloaded station air quality data collected from atmospheric monitors in the Destiny laboratory module.
Station Commander Sergey Ryzhikov and Flight Engineer Alexey Zubritsky, both Roscosmos cosmonauts, continued their gastrointestinal study scanning each other’s bellies with an ultrasound device after breakfast on Friday. Results from the experiment will help doctors understand how a crew member’s digestion, metabolism, and nutrient delivery adapt to weightlessness. The duo then split up to work on a variety of life support maintenance tasks throughout the station’s Roscosmos segment.
The SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft fired its Draco thrusters, located in the vehicle’s trunk, for 15 minutes on Friday reboosting the International Space Station’s orbit for the third time this month. The reboost maneuvers lifted the orbital outpost’s altitude to prepare for Soyuz crew swap operations later this year.
Learn more about station activities by following the space station blog, @space_station on X, as well as the ISS Facebook and ISS Instagram accounts.
Get the latest from NASA delivered every week. Subscribe here.
Powered by WPeMatico
Mark A. Garcia