Dragon Now Installed To Station For Month-Long Stay
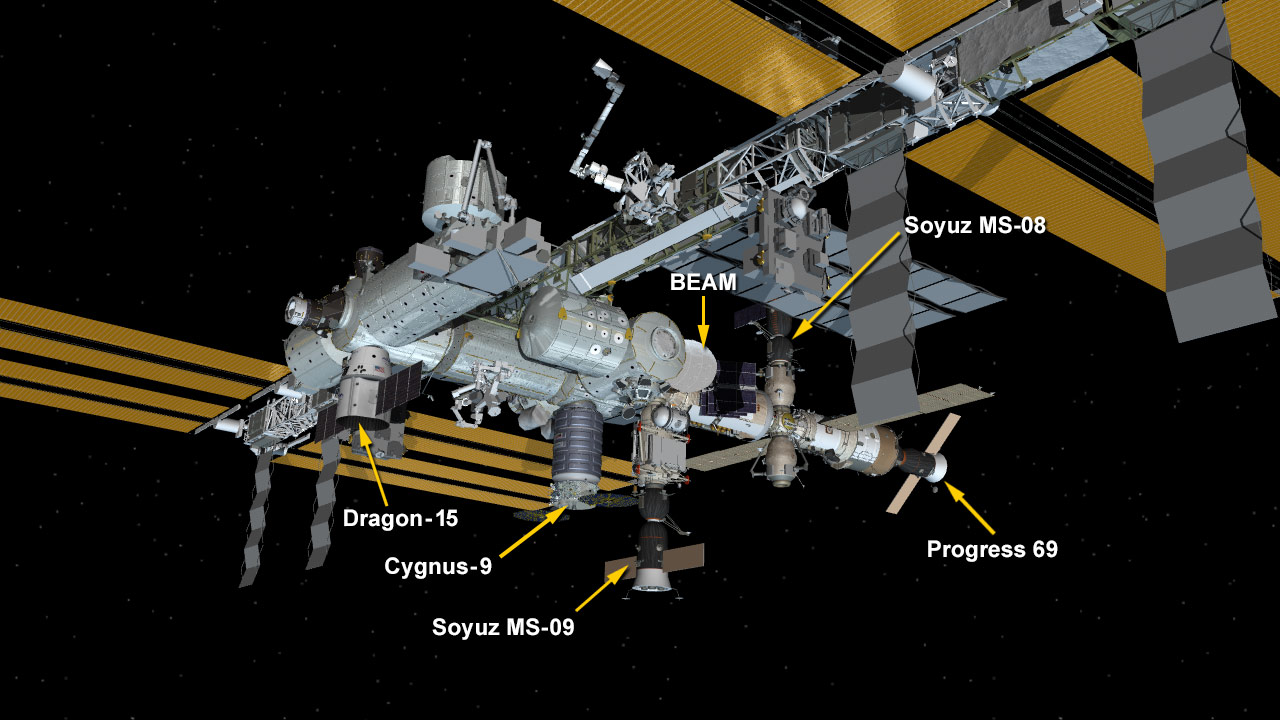
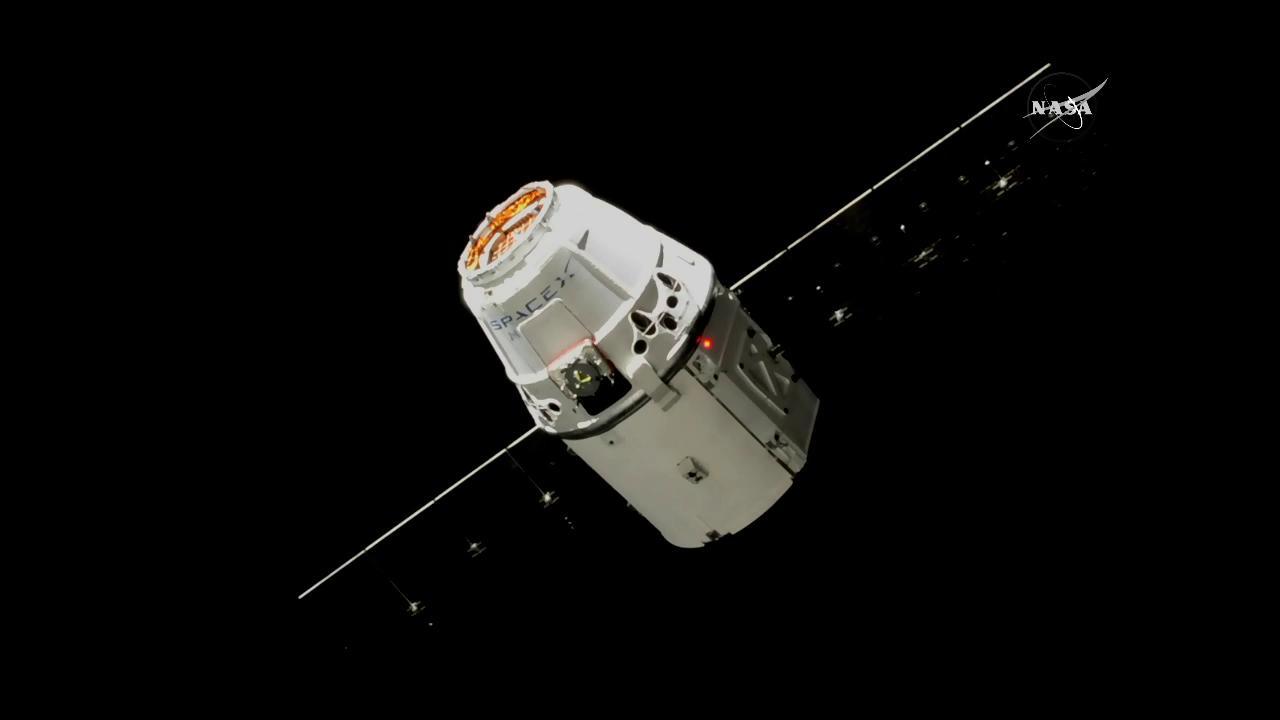
Three days after its launch from Florida, the SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft was installed on the Earth-facing side of the International Space Station’s Harmony module at 9:52 a.m. EDT.
The 15th contracted commercial resupply mission from SpaceX (CRS-15) delivers more than 5,900 pounds of research, crew supplies and hardware to the orbiting laboratory.
Among the research arriving to the U.S. National Laboratory is the Space Algae investigation, will discuss research to select algae strains adapted to space and sequence their genomes to identify growth-related genes. Algae consume waste carbon dioxide, can provide basic nutrition and may perceive microgravity as a trigger to produce algae oils rich in antioxidants that may help mitigate the harmful effects of microgravity and cosmic radiation during spaceflight. The Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS), which manages the U.S. National Laboratory, is sponsoring the investigation.
A technology demonstration arriving is an observational pilot study with the Crew Interactive MObile companioN (CIMON) that aims to provide first insights into the effects of crew support from an artificial intelligence (AI) in terms of efficiency and acceptance during long-term missions in space.
After Dragon spends approximately one month attached to the space station, the spacecraft will return to Earth with about 3,800 pounds of cargo and research, including an investigation to advance DNA sequencing in space and the Angiex cancer therapy investigation to improve understanding of endothelial cells that line the walls of blood vessels.
Keep up to date with the latest news from the crew living in space by following https://blogs.nasa.gov/spacestation/, @space_station and @ISS_Research on Twitter, and the ISS Facebook and ISS Instagram accounts.
Get The Details…
Mark Garcia
ISS
Powered by WPeMatico




